Table of Contents
Discovering Our Galactic Neighborhood
The realization that our solar system resides within the Orion Arm was a gradual process in the history of astronomy. Early civilizations, gazing up at the night sky, were unaware of the vast spiral structure of the Milky Way. It wasn’t until the 20th century, with advancements in radio astronomy and telescopic technology, that scientists could map our galaxy’s spiral arms. By analyzing the positions of stars and interstellar gas, astronomers identified the Orion Arm as the home of our Sun and many nearby stars. This discovery was a monumental step in understanding our place within the vast cosmos.
The Galactic Framework and Our Position
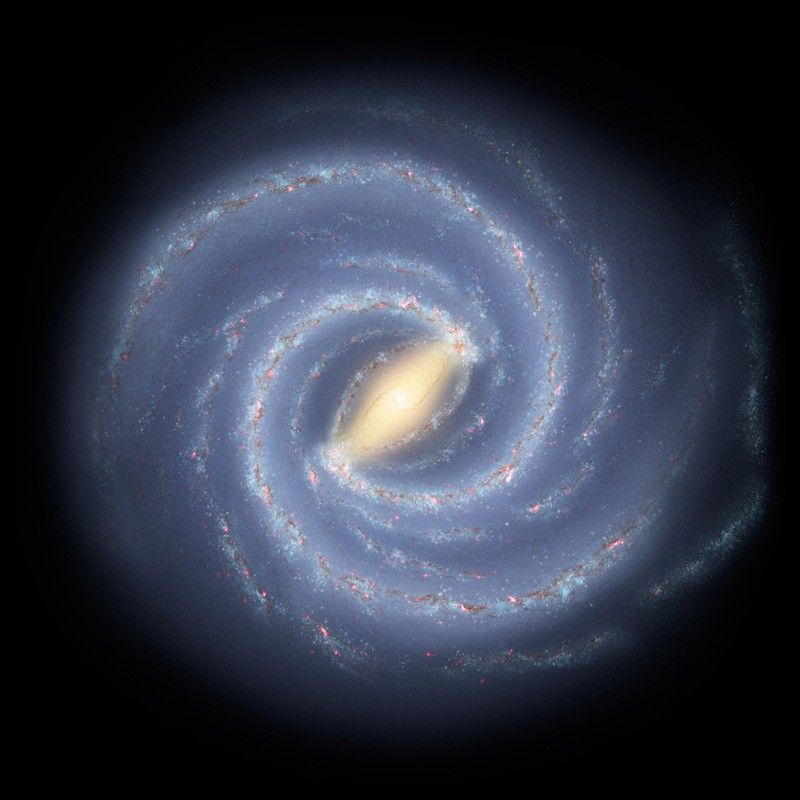
The Orion Arm, also known as the Orion Spur or Local Spur, is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy. It stretches approximately 3,500 light-years wide and 10,000 light-years long, nestled between the larger Sagittarius and Perseus arms. While it’s smaller compared to the major spiral arms, the Orion Arm is rich in star-forming regions, molecular clouds, and notable nebulae. It’s home to familiar stellar neighborhoods, including the Pleiades star cluster and the Orion Nebula, after which the arm is named. Our Sun is located near the inner edge of this arm, about 27,000 light-years from the galactic center.
Distinctive Features of Our Galactic Region
What sets the Orion Arm apart from other regions of the Milky Way is its status as a minor spur, rather than a primary spiral arm. Despite its smaller size, it hosts an impressive variety of stellar phenomena, including some of the galaxy’s most recognizable constellations, such as Orion, Taurus, and Canis Major. This region is also notable for its high concentration of both young, luminous stars and ancient, dimmer stars, offering a snapshot of different stages of stellar evolution. Furthermore, the Orion Arm contains a rich mix of gas and dust, making it a hotbed for ongoing star formation. These unique features make it an invaluable area for studying the complexities of galactic structure and evolution.
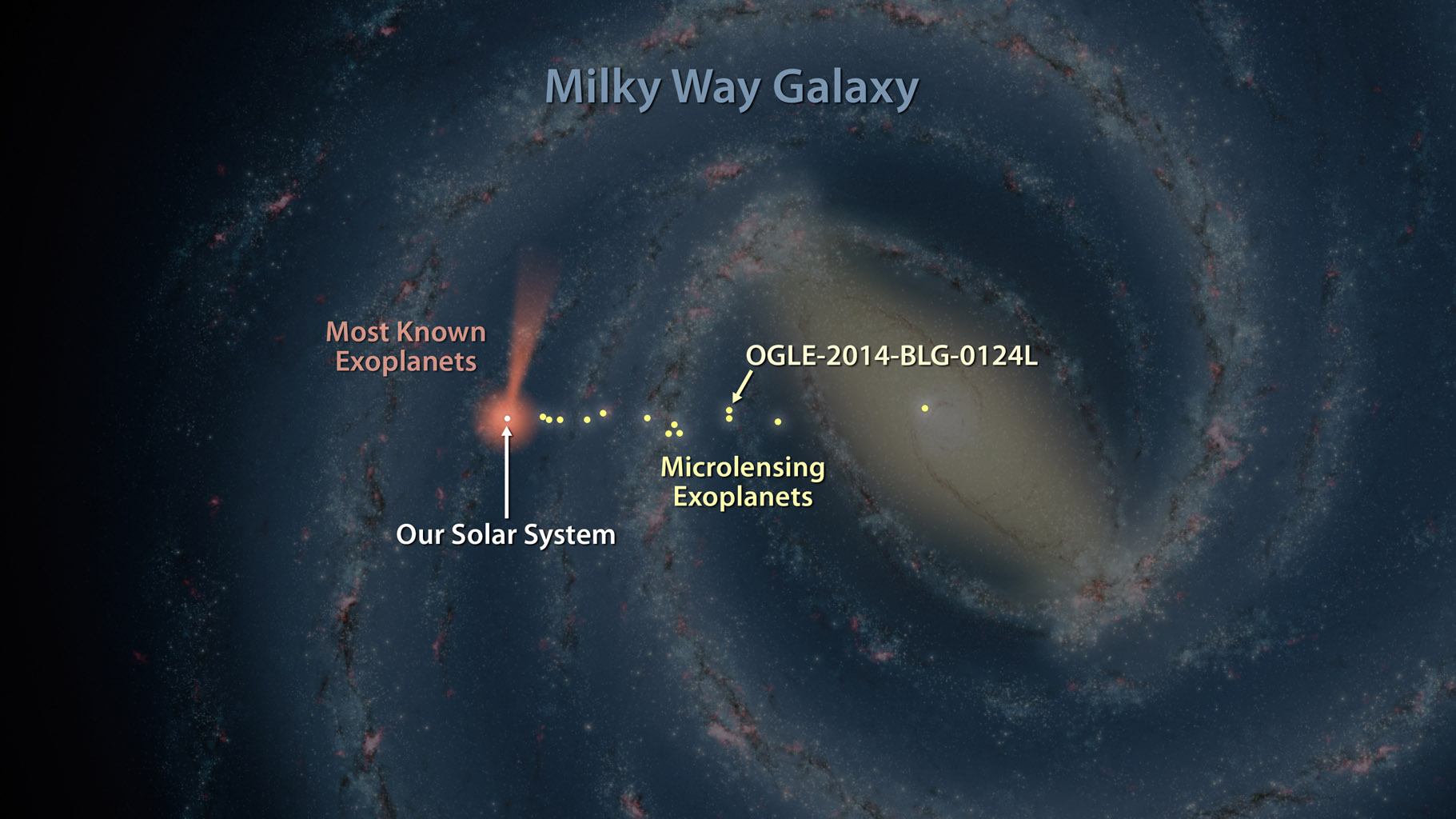
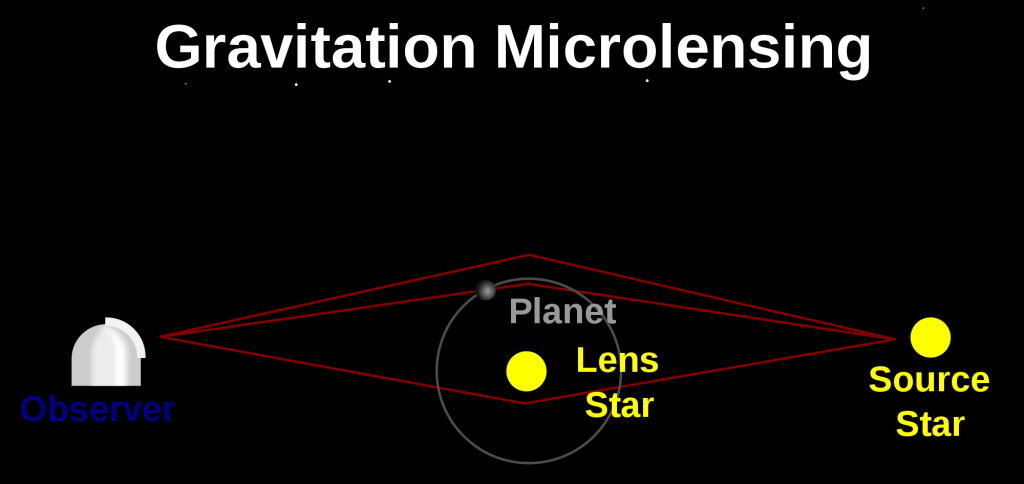
Mapping the Milky Way’s Spiral Arms
The Milky Way’s spiral structure remained elusive until the mid-20th century when radio astronomers began mapping hydrogen emissions from interstellar gas clouds. These emissions revealed the galaxy’s spiral arms, including the Orion Arm. The development of powerful telescopes and satellites like the Gaia spacecraft has allowed astronomers to map our galaxy with unprecedented precision. By studying the positions and movements of stars, scientists have refined our understanding of the Milky Way’s structure and confirmed our solar system’s location within the Orion Arm. This mapping continues today, offering new insights into our galaxy’s formation and evolution.
The Sun’s Journey Through the Orion Arm
Our Sun is not stationary within the Orion Arm; it orbits the center of the Milky Way at a speed of about 514,000 miles per hour. This journey takes roughly 225 million years to complete a single revolution—a period known as a “cosmic year.” The Sun’s current position in the Orion Arm places it near several star-forming regions and nebulae. As the solar system travels through the galaxy, it passes through varying interstellar environments, influencing cosmic ray exposure and potentially affecting Earth’s climate over geological timescales. Understanding this journey helps contextualize Earth’s place in cosmic history.
Notable Stellar Neighbors
The Orion Arm is home to many well-known stars and celestial objects. The Orion Nebula, a massive star-forming region, is one of the most prominent features and has given the arm its name. Other notable stars include Betelgeuse and Rigel in the Orion constellation, as well as Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, located in the constellation Canis Major. The Pleiades and Hyades star clusters also reside in this arm. These celestial landmarks have been studied for centuries, offering valuable insights into stellar evolution and the dynamic processes shaping our galaxy.
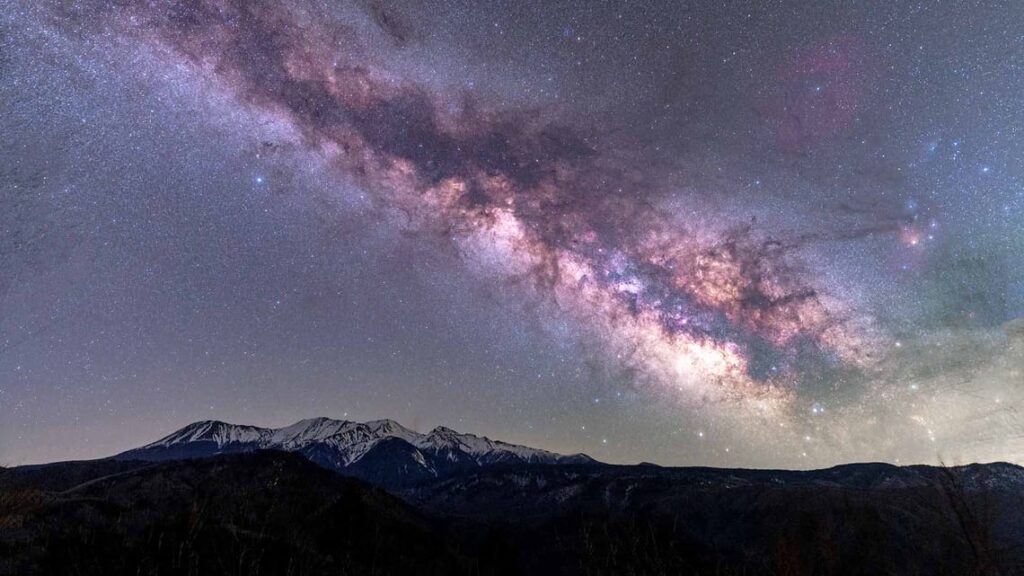

The Orion Arm and Star Formation
The Orion Arm is rich in regions of active star formation, driven by the abundance of molecular clouds and interstellar gas. The Orion Molecular Cloud Complex is one of the most studied star-forming regions, giving birth to massive stars that illuminate surrounding nebulae. The presence of these young, hot stars contributes to the arm’s brightness and makes it a focal point for astronomers. Studying these regions helps scientists understand the life cycle of stars, from their formation in dense clouds to their eventual death in supernova explosions. This process continuously enriches the interstellar medium with heavy elements.
The Role of the Orion Arm in Galactic Evolution
While the Orion Arm is considered a minor spiral arm, it plays a significant role in the Milky Way’s overall structure and evolution. The distribution of stars, gas, and dust within this arm influences the dynamics of our galaxy. The Orion Arm’s proximity to the larger Sagittarius and Perseus arms suggests it may serve as a bridge, facilitating the movement of material between these regions. Understanding the interactions between the Orion Arm and the rest of the galaxy helps scientists piece together the history of the Milky Way’s formation and the processes that shape spiral galaxies.
Cosmic Hazards in Our Galactic Neighborhood
Living in the Orion Arm comes with its share of cosmic hazards. The presence of massive stars and active star-forming regions increases the likelihood of nearby supernovae—explosions that can release intense radiation and cosmic rays. While Earth is currently in a relatively stable region, historical evidence suggests that past supernovae may have impacted our planet’s atmosphere and contributed to mass extinction events. Additionally, the solar system’s journey through the Orion Arm exposes it to varying interstellar environments, which could influence the heliosphere’s ability to shield Earth from cosmic radiation.
The Future of Our Solar System in the Orion Arm
As our solar system continues its journey through the Orion Arm, it will encounter new interstellar environments and cosmic phenomena. In the distant future, the Sun will move out of the Orion Arm and into different regions of the Milky Way, experiencing shifts in gravitational forces and cosmic radiation. These changes could have subtle effects on the solar system, influencing comet activity in the Oort Cloud or altering the orbits of distant objects. Understanding these future movements helps scientists predict the long-term evolution of our solar system and its interaction with the galaxy.
The Orion Arm in Modern Astronomy
Modern astronomy continues to unravel the mysteries of the Orion Arm using advanced technology and observational techniques. Space missions like the Gaia spacecraft have provided precise measurements of stellar positions and motions, refining our understanding of the Milky Way’s structure. Radio telescopes map hydrogen emissions, while infrared observatories like the James Webb Space Telescope peer through interstellar dust to study star formation. These efforts not only enhance our knowledge of the Orion Arm but also contribute to our broader understanding of spiral galaxies and the dynamic processes that shape them.

Our Place in the Universe
The discovery of our solar system’s location within the Orion Arm has profound implications for our understanding of the universe. It situates humanity within a vast, interconnected galaxy, highlighting our connection to the cosmos. The stars and nebulae of the Orion Arm serve as both scientific subjects and sources of inspiration, reminding us of our place in the universe. As we continue to explore and study our galactic neighborhood, we gain not only knowledge but also a deeper appreciation for the intricate beauty and complexity of the cosmos that surrounds us.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
Author
-
Meet Dr. Kendall Gregory, a highly accomplished professional with a remarkable academic background and a deep passion for empowering individuals through knowledge. Dr. Gregory’s educational journey began with a Bachelor of Science degree, followed by a Doctor of Chiropractic Medicine, focusing on diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal conditions. He further expanded his expertise with a Master's degree in Oriental Medicine, specializing in acupuncture and Chinese herbology, and a Master's degree in Health Care Administration, emphasizing his dedication to improving healthcare systems. Dr. Gregory combines his extensive knowledge and practical experience to provide comprehensive and integrative healthcare solutions. Through his writings, he aims to inspire individuals to take charge of their health and make informed decisions.
View all posts








I like that video, wild how we figured out where we are in the Milky Way.